In this course we consider the intersection of:
- The Environment (earth surface, atmosphere, life (including human))
- Media (representations of the environment, how media works: contains messages, assumptions, theories, persuasive power)
Today we are going to start with some contextual information about the environment. Please read through this page paying particular attention to the way data is represented in the images/diagrams – media includes data visualization. Click on links, watch the short videos you find. At the end there is a short introduction to issues and topics on media and the environment, and some environmental media projects for you to browse, including two ~20 minute podcasts. Enjoy!
Environmental Context: Deep History of the Earth
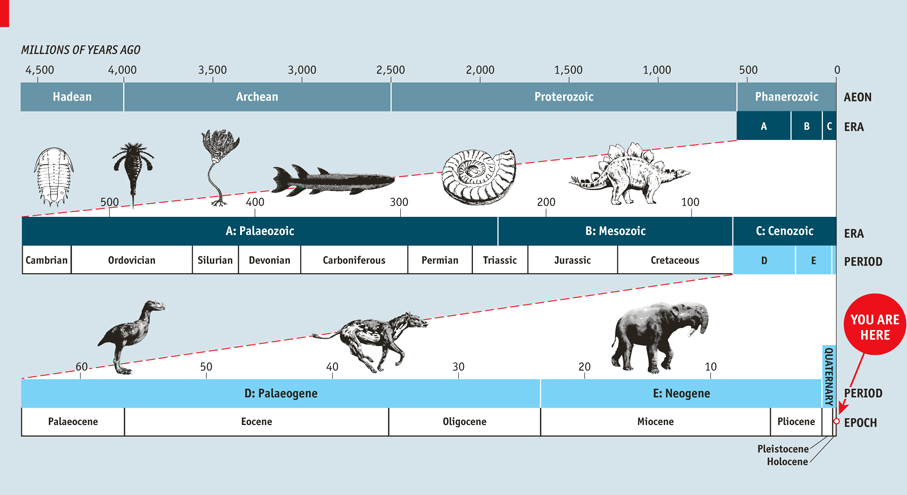
from “A man made world,” The Economist, 28 May 2011
- Age of Earth 4.5 billion years, (Age of Universe 13.8 billion)
- geological periods are convenient and conventional, note how time-spans are put into a hierarchy
- note media representation above, especially difficulty of representing vast time scales AND much smaller time scales
- why/is the diagram above a good representation? look carefully and critically at all diagrams/images, think about how the data is visualized.
- How do they/we know the age of the earth?
- stratigraphy (study of rock layers) and fossil record (evidence gathered from late 1600s to now) – early estimate of earth’s age about 8,000 years, relative age arrived at first, absolute dates much later.
- radiometric dating (based on decay of radioactive isotopes), Marie and Pierre Curie discover radium 1898. technique starts in 1905 and improves.
- plus other methods, annual layers of sediments (varves), ice-cores (count like tree rings))
By User:LennyWikidata [CC BY 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
- Early Supercontinents – Gondwana etc.
- fossil evidence found tropical plants in northern latitudes, geologists begin to suspect land masses moved
- 1960s: after much controversy the theory of Plate Tectonics became widely accepted – continents have moved, land masses split and reformed. (Wegener etc.)
- animation of plate movement 200 million years ago -> now

atmospheric composition, from scientific psychic
- Earth’s Atmosphere: has it always been the same? No
- Early atmosphere – no oxygen
- Description/Analysis of Diagram – pros and cons?
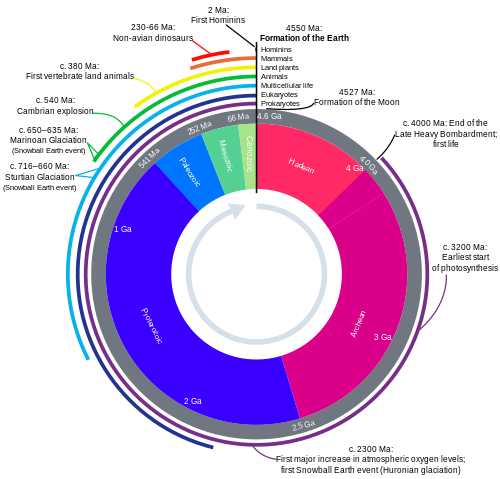
timeline of life, wikimedia commons
- Life on Earth
- First life at 3.8 billion years = prokaryote one cell creatures in atmosphere without oxygen.
- note Prokaryote/Eukarote difference – cells with no nucleus (bacteria) versus cells with nucleus + organelles
- note when Photosynthesis starts (c. 3200 MA)
- Look carefully to understand what the different rings represent.
- Description/Analysis of Diagram – is the first image or this one better at visualizing this time scale?
- How do we know about Life on Earth?
- Fossil Record -> Theory of Evolution, 1859 Darwin’s Origin of Species
- Microscopic examination of fossil record from the late 1800s
- DNA (genetics, molecular biology etc) 1953 Crick and Watson based on work of Rosalind Franklin
- Note : Historical versus causal understanding.
- we can be fairly certain about reconstruction of events – fossil record etc.
- but theories about causation may change and evolve.
- Theory of Evolution, 1800s,
- Theory of Plate Tectonics 1950-70
- First Mass Extinction? 2.4 billion years ago = Great Oxygenation Event
- amount of O2 in atmosphere grows
- why? growth of cyanobacteria -> waste product oxyygen
- anaerobic become extinct -> aerobic organism
- Mass Extinction Events, caused by volcanic activity, changes in climate/atmosphere, meteors
- 439 million years ago, 86% of life made extinct
- 364 million years ago 75%
- 251 million years ago, 96%
- between 199 million and 214 million years ago, 50% animals extinct, plants less affected
- 65 million years ago, End of Dinosaurs + 76% of life on earth . volcanic activity, asteroid impact, and climate change

Guardian Graphic
- Anthropocene – a new epoch (smallest time-span) after holocene?
- Diagram from Guardian Article, Aug 29, 2016
- “Anthropocene” being considered as a formally defined geological unit by by a Working Group for the International Commission on Stratigraphy.
- Identifying measurable human impact on world systems e.g.
- Climate Change
- Atmospheric changes
- Mass Extinction Number 6 – dead oceans, loss of habitats, overfishing etc etc.
- 30 to 50 percent of all species possibly heading toward extinction by mid-century
- who have I linked to, what are their credentials? where does number above come from?
- Pollution – plastic layer in the world

Diagram from the Smithsonian: The Age of Humans: Evolutionary Perspective on the Anthropocene
**********
Media and the Environment
- Representations of the environment in all kinds of media have changed drastically over the last few hundred years
- nature as threat, 1700s
-
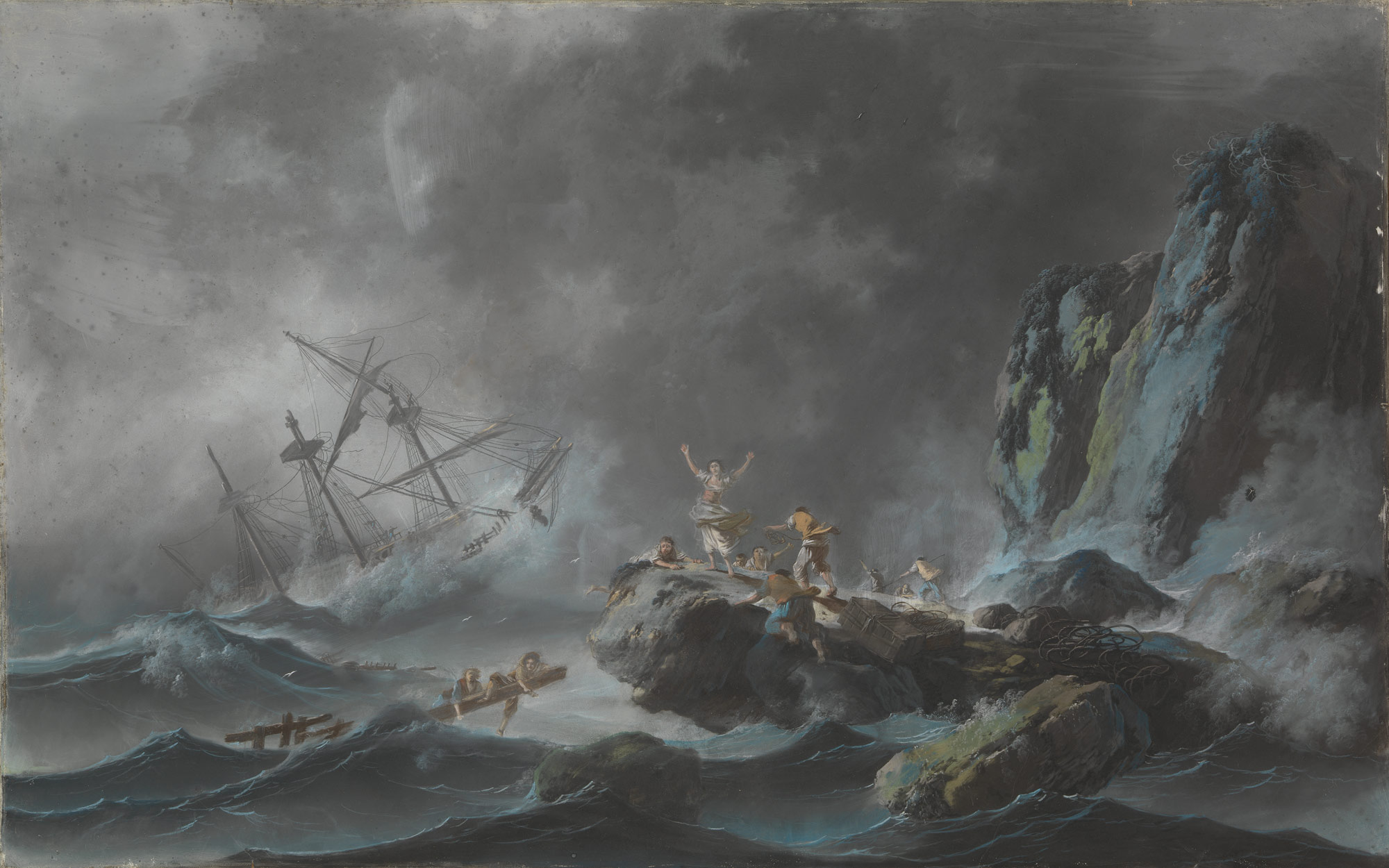

A shipwreck in a Storm Jean Pillement
- nature as threatened, 2000s
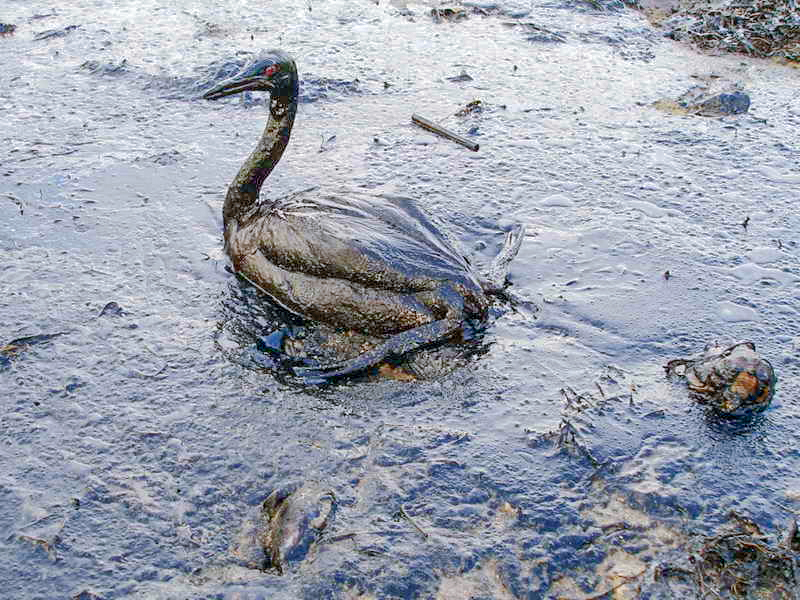

By Marine Photobank – originally posted to Flickr as Oiled Bird – Black Sea Oil Spill 11/12/07, CC BY 2.0, Link
- We will look at many kinds of media/genres
- film, games, data visualizations/animations, social media, news/docs
- We will consider how media works by evoking
- referential systems: connotations, metaphors, associations, contradictions
- cognitive systems: emotions, reason, affect (gut reactions)
- We will consider how environmental issues are framed/controlled/created in media
- the relationship between form/content
- the persuasive and normalizing power of media
- role of media as part of change/activism
- Finally – two examples of environmental media
- The Hive by Wolfgang Buttress, browse site and watch video
- Midway, a Message from The Gyre by Chris Jordan, context Great Pacific Garbage Patch, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- And two Podcasts (~20 mins each)
References:
Martin Rudwick, Earth’s Deep History,University of Chicago Press, 2014